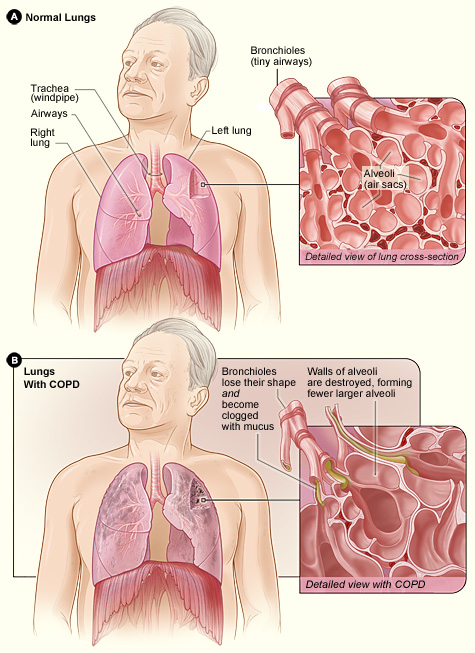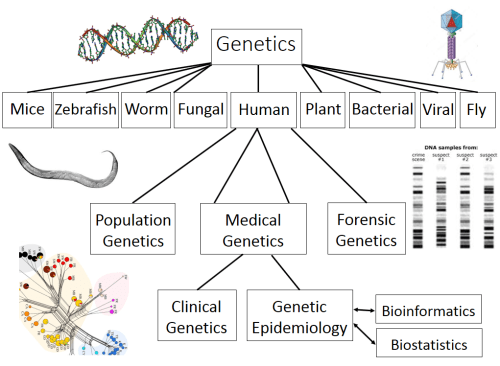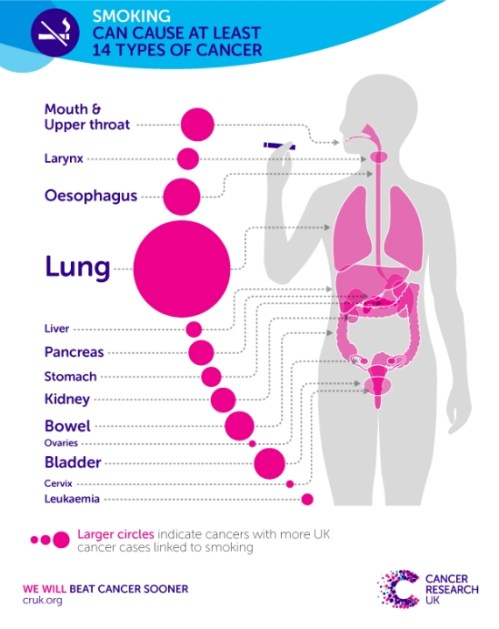
We now know that, through studies carried out by many natural scientists over decades, smoking is a (considerable) risk factor for many cancers and respiratory diseases; but the public ignore these findings and keep smoking, which is where social scientists can help facilitate in getting the message across. Just one example of where the social sciences can have a massive (positive) impact on society. Image taken from stopcancer.support
“
Scientists focus relentlessly on the future. Once a fact is firmly established, the circuitous path that led to its discovery is seen as a distraction.” – Eric Lander in the
Cell journal (Jan 2016)
As scientists in the ‘natural’ sciences (e.g. genetics, physics, chemistry, geology), we have to make observations in the real world and think of hypotheses and models to make sense of it all. To test our hypotheses, we then have to collect (sufficient amounts of) data and see if the data collected fit the results that our proposed model predicted. Our hypotheses could be described as our ‘prejudice’ towards the data. However, we then have to try and counteract (and hopefully eliminate) our biases towards the data by performing well-designed experiments. If the results backup our predictions, we of course become (very!) happy and try to (replicate and then) publish our results. Even then (i.e. after a paper has been submitted to a journal), there is a lot left to do as the publication process is a long-winded one with many rounds of ‘peer-reviewing’ (an important quality control mechanism), where we have to reply fully to all the questions, suggestions and concerns the reviewers throw at us about the importance of the results, reliability of the data, the methods used, and the language of the manuscript submitted (e.g. are the results presented in an easy-to-understand way, are we over-sensationalising the results?). If all goes well, the published results from the analyses can help us (as the research community) understand the mechanisms behind the phenomenon analysed (e.g. biological pathways relating to disease, underlying mechanism of a new technology) and provide a solid foundation for other scientists to take the work forward.
If the results are not what we expected, a true scientist also feels fortunate and becomes more driven as a new challenge has now been set, igniting the curious side of the scientist; and strives to understand if anything may have gone wrong with the analysis or that whether the hypothesis was wrong. A (natural) scientist who is conscious and aware of the evolution and history of science knows that many discoveries have been made through ‘happy accidents’ (e.g. penicillin, x-ray scan, microwave oven, post-it notes) since it is in the nature of science to be serendipitous; and that a wrong hypothesis and/or an unexpected result can also lead to a breakthrough. Hopefully without losing any of our excitement, we go back to square one and start off with a brand new hypothesis (NB: the research paradigm in some fields is also changing, with ‘hypothesis-free’ approaches already been, and are being developed). This process (i.e. from generating the hypothesis to data collection to analysis to publication of results) usually takes years, even with some of the brightest people collaborating and working full-time on a research question.
“The first time you do something, it’s science. The second time, it’s engineering. A third time, it’s just being a technician. I’m a scientist. Once I do something, I do something else.” – Cliff Stoll in his TED talk (Feb 2006)
Natural scientists take great pride in exploring nature (living and non-living) and the laws that govern it in a creative, objective and transparent way. One of the most important characteristics of publications in the natural sciences is repeatability of the methods and replication of the results. I do not want to paint a picture where everything is perfect with regards to the literature in the natural sciences, as there has always been, and will be, problems in the way some research questions have been tackled (e.g. due to poor use of statistical methods, over-sensationalisation of results in lay media, fraud, selective reporting, sad truth of ‘publish or perish’, unnecessary number of co-authors on papers). However science evolves through mistakes, being open-minded about accepting new ideas and being transparent about the methods used. Natural scientists are especially blessed with regards to there being many respectable journals (with relatively high impact factors, 2 or more reviewers involved in the peer-reviewing process) in virtually all fields within the natural sciences, where a large number of great scientific papers are published; and these have clearly (positively) affected the quality of life of our species (e.g. increasing crop yield, facilitating understanding of diseases and preventive measures, curative drugs/therapies, underlying principles of modern technology).
I wrote all the above to come to the main point of this post: I believe the abovementioned ‘experiment-centric’ (well-designed, statistically well-powered), efficient (has real implications) and reliable (replicable and repeatable) characteristics of the studies carried out within the natural sciences should be made more use of in (and probably become a benchmark for) the social sciences. There should be a more stringent process before a paper/book is published similar to the natural sciences, and a social scientist must work harder (than they are doing at current) to alleviate their own prejudices before starting to write-up for publication (and not get away with papers which are full of speculation and sentences containing “may be due/related to”). I am not even going to delve into the technicalities of some of the horrendously implemented statistical methods and the bold inferences/claims made as a result of them (e.g. correlations/associations still being reported as ‘causation’, P-values of <0.05 used as 'proof').
Of course there are great social scientists out there who publish some policy-changing work and try to be as objective as a human being can possibly be, however I have to say that (from my experience at least!) they seem to be a great minority in an ocean of bad sociologists. Social sciences seem (to me!) to be characterised by subjective, incoherent and inconsistent findings (e.g. due to diverse ideologies, region-specific effects, lack of collaboration, lack of replication); and a comprehensive quality control mechanism does not seem to be in place to prevent bad literature from being published. A sociologist friend had once told me “you can find a reference for any idea in the social sciences”, which I think sums up the field's current state for me in one sentence.
“The scientist is not a person who gives the right answers, he’s one who asks the right questions.” – Claude Lévi-Strauss, an anthropologist (I would humbly update it as “The scientist is not necessarily a person who gives the right answers, but one who asks the right questions”)
Social sciences should not be the place where ones who could not (get the grades and/or) be successful in the natural sciences go to and get a (relatively) easier ride; and publish tens of papers/books which go insufficiently peer-reviewed, unread and uncited for life; but get a lecturer post at a university much quicker in relation to a natural scientist. Social scientists should not be any different from natural scientists with regards to the general aspects of research, so they should also spend years (just like most natural scientists) trying to develop their hypotheses and debunk their own prejudices; work in collaboration with other talented social scientists who will guide them in the right way; and be held accountable to a stringent peer-reviewing process before they can claim to have made a contribution (via books/papers) to their respective fields. Instead of publishing loads of bad papers, they should be encouraged to and concentrate on publishing fewer but much better papers/books.
Social sciences have a lot to offer to society (see the above figure about smoking for an example), but unfortunately (in my opinion) the representatives have let the field down. I believe universities and maybe even the governments all around the world should make it their objective to develop great sociologists by not only engaging them with the techniques used in the social sciences (and its accompanying literature), but also by funding them to travel to other laboratories/research institutions and get a flavour of the way natural scientists work.
Addition to post: For an academically better (and much harsher!) criticism of the social sciences than mines, see Roberto Unger’s interview at the Social Science Bites website (click on link).

Moon landing – a momentous achievement of mankind, and the natural sciences (and engineering)
PS: I must state here that I have vastly generalised about the social sciences; and mostly cherry picked and pointed out the negative sides. However every sociologist knows within them whether they really are motivated to find out the truth about sociological phenomena; and are not just in it for the respect that being an academic brings, or for the titles (e.g. Dr., Prof.). I personally have many respectable sociologist friends/colleagues myself (including my father) who are driven to understand and dissect sociological problems/issues and look for ways to solve real-life problems. They give me hope in that sense…
PPS: I am not an expert in the natural sciences nor in the social sciences. Just sharing my (maybe not so!) humble opinions on the subject matter as I get increasingly frustrated with the lack of quality I observe throughout the social sciences. Many of my friends/colleagues in the social sciences would attest to some or all of the things I stated above (gathering from my personal communications). I value the social sciences a lot and want it to live up to its potential in making our communities better…
Read Full Post »